An evolutionary biology term that refers abstractly to an unknown set of genetic codes that result in a phenotype. Evolutionary biologists reason with genotypes and phenotypes, positing that they must exist even though the revelation of the actual mechanics of genetics has greatly complicated the old Darwinian paradigm.
Neuromythopedia
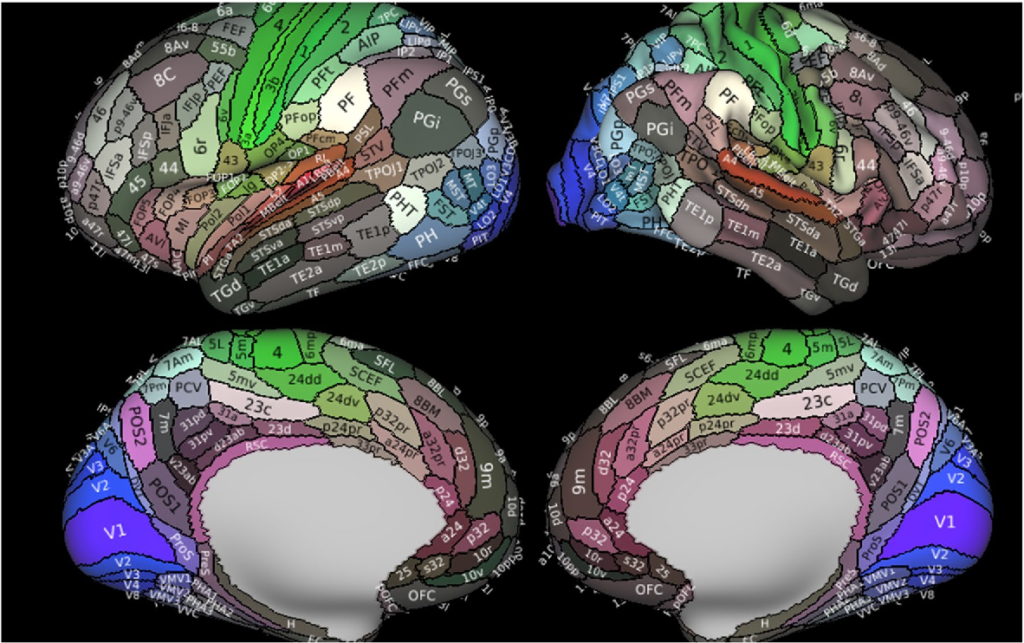
Matthew Glasser, David van Essen, et al published a parcellation of the human brain in 2016, based on fMRI data collected during their earlier Human Connectome Project.
https://www.nature.com/articles/nature18933
This parcellation is used as the foundation of the Neuromythograph model for the cortex. The Allen Brain Atlas is the foundation of the subcortical components of the Neuromythograph.
Reference maps of the brain have historically been hampered by variability from person to person. No two brains are shaped the same, and this goes for the individual brain areas as well. The Glasser parcellation represented a breakthrough because its map can be reliably overlaid on the brain of any human. The shapes of the areas may be distorted, but the topological relationships between adjacent areas are consistent. This replicability across people offers promise that neuromythographic interpretations can also be used to interpret fMRI scans across human subjects.
Gnosis signifies a knowledge or insight into humanity’s real nature as divine, leading to the deliverance of the divine spark within humanity from the constraints of earthly existence.
From: Wikipedia
A graph database is a type of database that models relations between entities. In graph theory (a branch of mathematics), these relations are called edges, and the entities themselves are called vertices or nodes.